The Power Players: Understanding OPEC’s Influence in the Global Oil Market
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) has been a central player in the global oil market for over six decades. As a consortium of major oil-exporting nations, OPEC’s primary mission is to coordinate and unify petroleum policies among member countries, ensuring stable oil markets and fair returns on investments. This blog explores OPEC’s role in shaping the global oil landscape, its influence on oil prices, and its strategic responses to market challenges.
The Formation and Evolution of OPEC
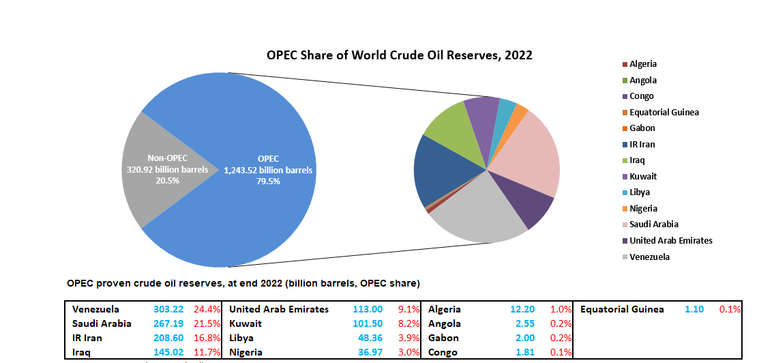
OPEC was established in 1960 by five founding members: Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela. Over the years, the organization has expanded to include 13 member countries, primarily from the Middle East, Africa, and South America. OPEC’s headquarters is in Vienna, Austria.
Core Objectives of OPEC
OPEC aims to:
- Stabilize Oil Markets: By coordinating production levels, OPEC seeks to avoid excessive fluctuations in oil prices, ensuring a stable supply for consumers and fair returns for producers.
- Secure Fair Prices: OPEC strives to achieve a balanced and fair price for oil, which is beneficial for both producers and consumers.
- Manage Oil Supply: Through production quotas and collective agreements, OPEC manages the supply of oil to align with global demand, preventing oversupply or shortages.
Mechanisms of Influence
1. Production Quotas:
- OPEC sets production targets for its member countries, adjusting output levels to influence global oil supply and stabilize prices. These quotas are determined based on market conditions, economic forecasts, and geopolitical considerations.
2. Market Monitoring:
- OPEC continuously monitors global oil markets, analyzing data on supply, demand, inventories, and price trends. This information guides the organization’s decisions on production adjustments and market interventions.
3. Collaborative Agreements:
- In recent years, OPEC has collaborated with non-OPEC oil-producing countries, forming the OPEC+ alliance. This broader coalition, which includes major producers like Russia, aims to enhance market stability through coordinated production cuts or increases.
Impact on Oil Prices
OPEC’s decisions on production levels have a significant impact on global oil prices:
- Supply Cuts: When OPEC reduces production, it decreases the global supply of oil, which typically leads to higher prices if demand remains constant or increases.
- Supply Increases: Conversely, when OPEC increases production, it can lead to an oversupply of oil, resulting in lower prices if demand does not keep pace.
Geopolitical Influence
OPEC’s actions are often influenced by geopolitical factors, including:
- Regional Conflicts: Political instability and conflicts in key oil-producing regions can disrupt production and supply, prompting OPEC to adjust output to stabilize markets.
- Sanctions and Trade Policies: International sanctions and trade policies affecting member countries, such as those imposed on Iran and Venezuela, can impact production levels and market dynamics.
- Global Economic Conditions: Economic growth or recession in major economies influences oil demand, prompting OPEC to adjust production to maintain market balance.
Challenges and Criticisms
OPEC faces several challenges and criticisms:
- Market Share and Competition: The rise of shale oil production, particularly in the United States, has increased competition and reduced OPEC’s market share. Technological advancements in extraction have made non-OPEC oil more accessible and economically viable.
- Internal Disagreements: Differences in economic priorities and production capacities among member countries can lead to internal conflicts and difficulties in reaching consensus on production targets.
- Environmental Concerns: Global efforts to combat climate change and transition to renewable energy sources pose long-term challenges to OPEC’s relevance and influence in the global energy market.
Strategic Adaptations
To address these challenges, OPEC has adopted several strategic adaptations:
- OPEC+: The formation of the OPEC+ alliance has strengthened OPEC’s influence by including major non-OPEC producers in production agreements, enhancing the organization’s ability to stabilize markets.
- Diversification Efforts: Some OPEC member countries are investing in economic diversification and renewable energy to reduce their dependence on oil revenues and adapt to changing energy landscapes.
- Market Flexibility: OPEC has shown increased flexibility in responding to market conditions, adjusting production targets more frequently and engaging in dialogue with key stakeholders to maintain market stability.
Conclusion
OPEC’s role in the global oil market is multifaceted, involving strategic production management, market monitoring, and geopolitical navigation. Despite facing significant challenges, OPEC continues to exert considerable influence over oil prices and market stability. By understanding OPEC’s mechanisms of influence and strategic responses, stakeholders can better anticipate market trends and make informed decisions in the dynamic world of global oil. As the energy landscape evolves, OPEC’s ability to adapt and collaborate will be crucial in maintaining its relevance and effectiveness in shaping the future of energy markets.